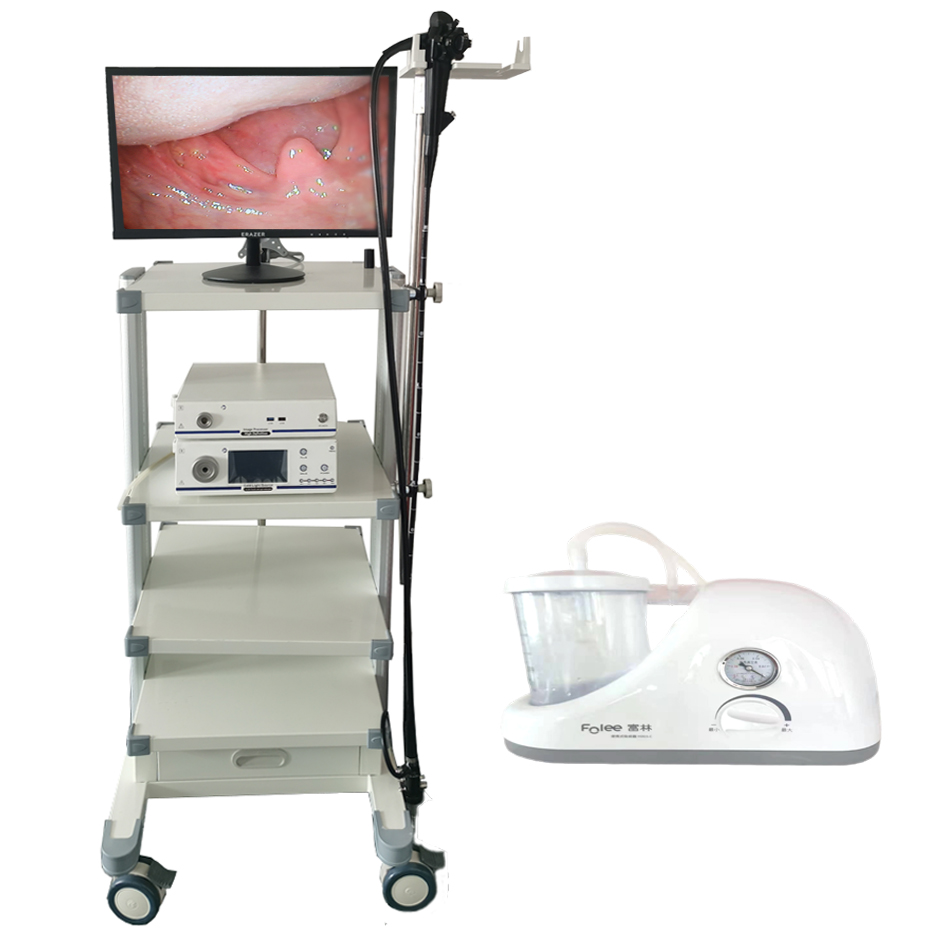
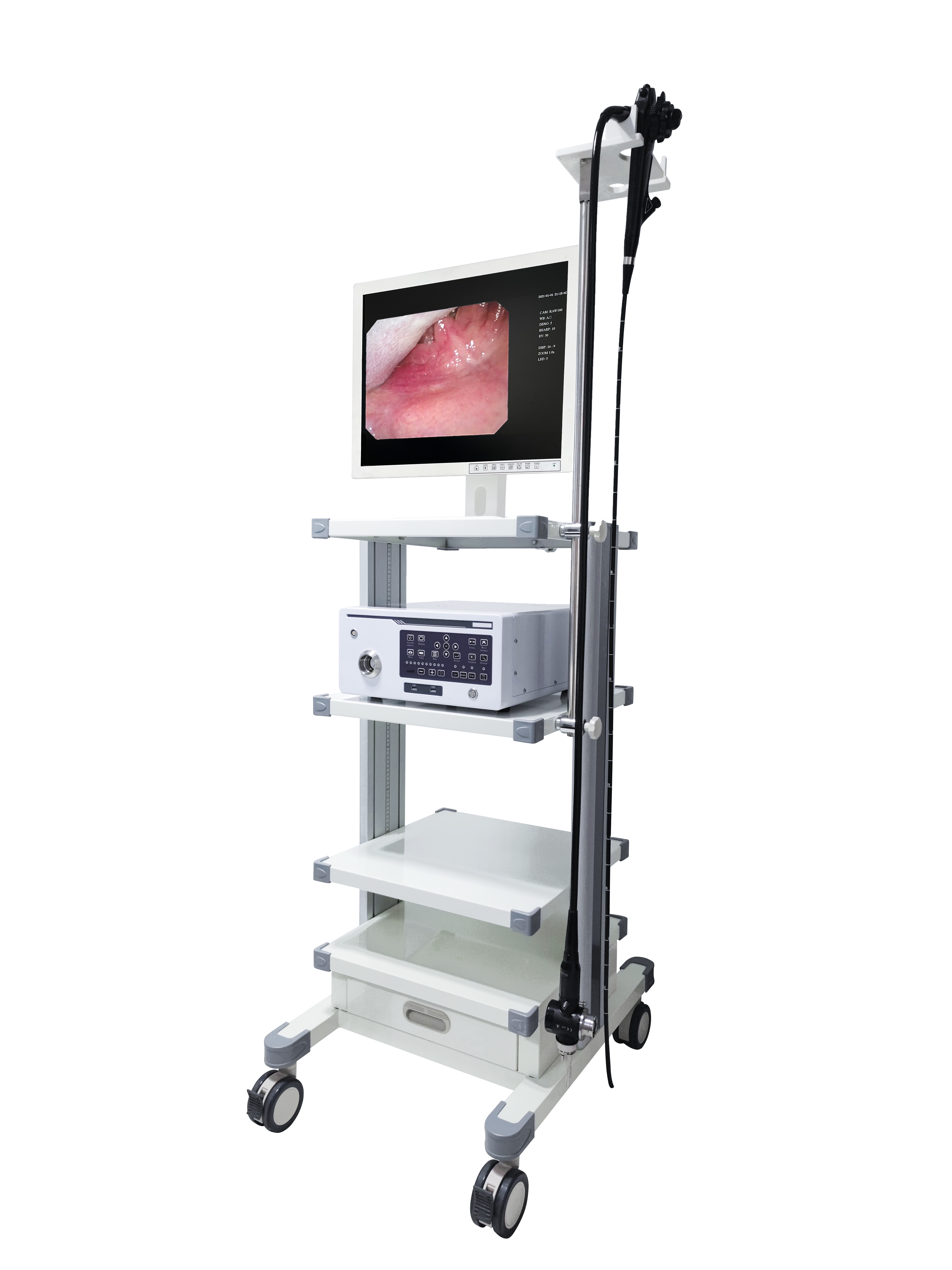
The field of veterinary medicine has seen significant advancements in recent years, with many technological innovations revolutionizing animal care. One such groundbreaking tool that has greatly contributed to the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions in animals is the veterinary endoscope. In this blog, we will delve into the world of veterinary endoscopes, exploring their working mechanisms, benefits, and applications in modern veterinary practices.
What is a Veterinary Endoscope?
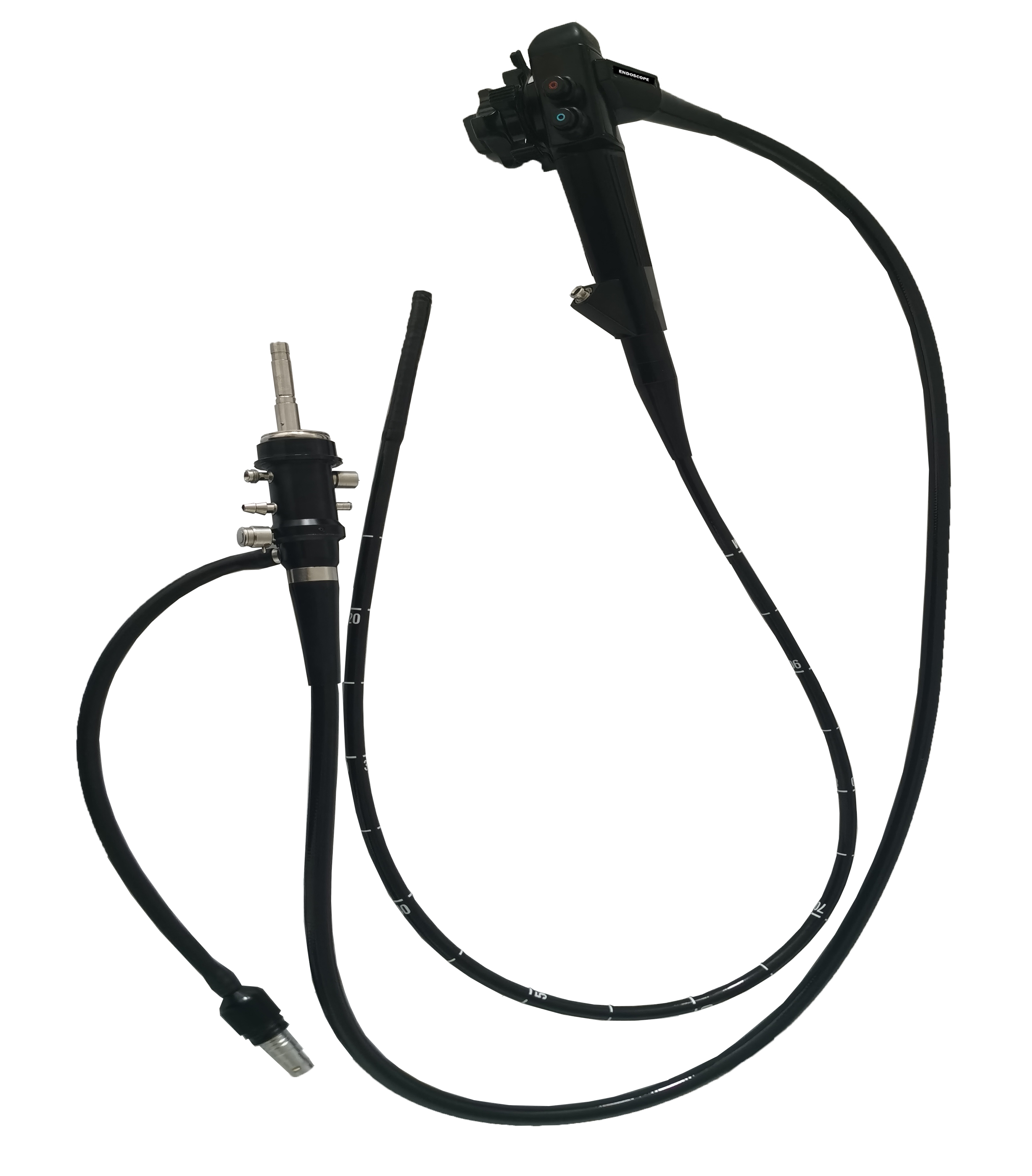
A veterinary endoscope is a specialized medical device that consists of a long, flexible tube with a light source and a camera attached to its end. It allows veterinarians to visualize and access hard-to-reach areas within an animal’s body, such as the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, and urinary tract. The images captured by the camera are displayed on a monitor, enabling veterinarians to closely examine the internal structures of animals without the need for invasive procedures.
Veterinary endoscopes operate on the principle of minimally invasive procedures. The endoscope is carefully inserted into the appropriate body cavity through natural orifices or small incisions. The light source illuminates the area, while the camera transmits high-definition images to the monitor in real-time. This allows veterinarians to visualize abnormalities, take biopsies, retrieve foreign objects, or perform certain surgical procedures with precision and minimal discomfort to the animal.
Benefits of Veterinary Endoscopy:
1. Less invasive procedures: Compared to traditional surgery, endoscopy significantly reduces the invasiveness of procedures. This has numerous advantages, including reduced pain, shorter recovery times, and minimized risk of complications.
2. Accurate diagnosis: Veterinary endoscopes provide clear and detailed visualizations of internal structures, enabling veterinarians to accurately diagnose various conditions. This allows for early detection and timely intervention, leading to improved treatment outcomes.
3. Minimizing risks: By avoiding extensive incisions or construction of body cavities, endoscopy minimizes the risk of infections and complications associated with conventional surgeries, leading to a faster and safer recovery for animals.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
1. Gastrointestinal evaluation: Endoscopy plays a pivotal role in evaluating gastrointestinal disorders such as ulcers, polyps, tumors, or foreign bodies. It allows veterinarians to directly visualize and assess these conditions, guiding appropriate treatment plans.
2. Respiratory examination: Veterinary endoscopes are used to inspect the airways and lungs, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory conditions like pneumonia, tracheal collapse, or bronchitis.
3. Urinary system evaluation: Endoscopy enables veterinarians to visualize the urinary tract, including the bladder and urethra, to diagnose and treat conditions like bladder stones, tumors, and urethral obstructions.
Conclusion:
The veterinary endoscope has emerged as a game-changer in the field of veterinary medicine. With its ability to provide non-invasive assessments, accurate diagnoses, and precise treatments, this cutting-edge technology offers immense benefits for animals. By embracing the use of veterinary endoscopes, veterinarians can elevate the standards of care, ultimately improving the well-being and quality of life for their furry patients.
Post time: Nov-10-2023